How does a hydropower plant create electricity?
- A continuous stream of water is diverted from a river or lake into a penstock.
- Inside the penstock, the flow of water spins a turbine.
- That turbine spins a generator.
- The generator uses a magnetic field and motion to create electricity.
- This electricity is then sent to the local utility grid.
- The utility grid sends electricity through power lines to houses, schools, and businesses in the community.
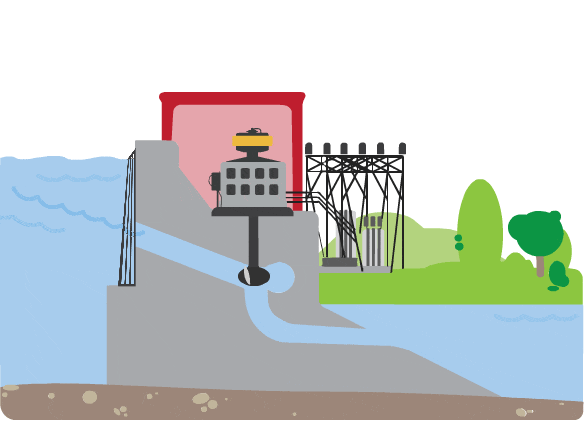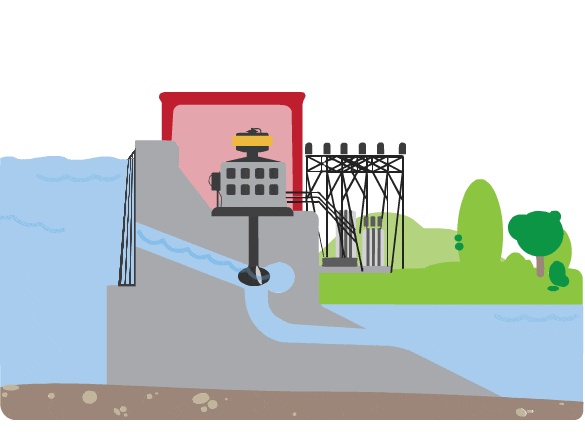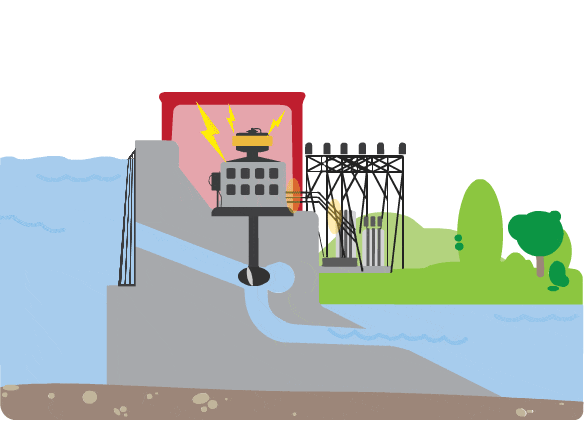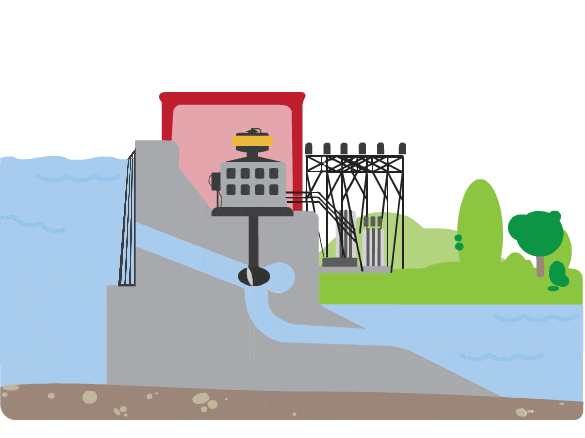
What does a turbine look like?
Kaplan

Pelton

Francis

Where does the water come from?
The hydrologic cycle describes water’s continuous journey around the earth as it transforms into solid, liquid, and gas. While shifting forms, water travels between oceans, atmosphere, and land by many different processes. These processes can be viewed below:
- Evaporation & Condensation (humidity & the forming of clouds)
- Precipitation (snow & hail)
- Snowmelt and runoff (spring rivers)
- Transpiration & Condensation (vapor from plants & the forming of fog)
- Precipitation (rain)
- Groundwater & Surface Flow (underground streams & above ground floods)

As weather and geographic conditions are not the same in all areas of the world, many regions do not experience these processes in equal amounts.
For example: a place close to the equator, like Hawaii, experiences rain, fog, and dew almost daily, but may only get a tiny bit of snow (at the very top of a volcano) every 5 years.

